Case Study: Curcumin
Curcumin is a bright yellow, naturally occurring chemical compound. It is a hydrophobic polyphenol and the main active constituent of turmeric. Classified as a class IV drug by the biopharmaceutical system (BCS), curcumins bioavailability is commonly enhanced by utilizing adjuvants like piperine, which inhibits its metabolic pathway. The compound has been credited with a wide spectrum of pharmacological properties for the prevention and treatment of several chronic diseases, such as cancer, autoimmune diseases, diabetes and skin diseases.


The most challenges using this drug therapeutically are the hydrophobic properties of Curcumin, thereby its limited bioavailability, and rapid metabolism. A Marinosolv®-enabled curcumin formulation at concentrations of at least 3mg/ml dissolved Curcumin may solve this problem and opens several opportunities in a growing demand in the market.
Further enabled compounds
Marinosolv® enables the solubilization of APIs from mainly BCS (biopharmaceutics classification system) classes II and IV. Marinomed has validated the technology through its own product development projects, improving established APIs. Furthermore, several compounds have been solubilized successfully in different client projects.
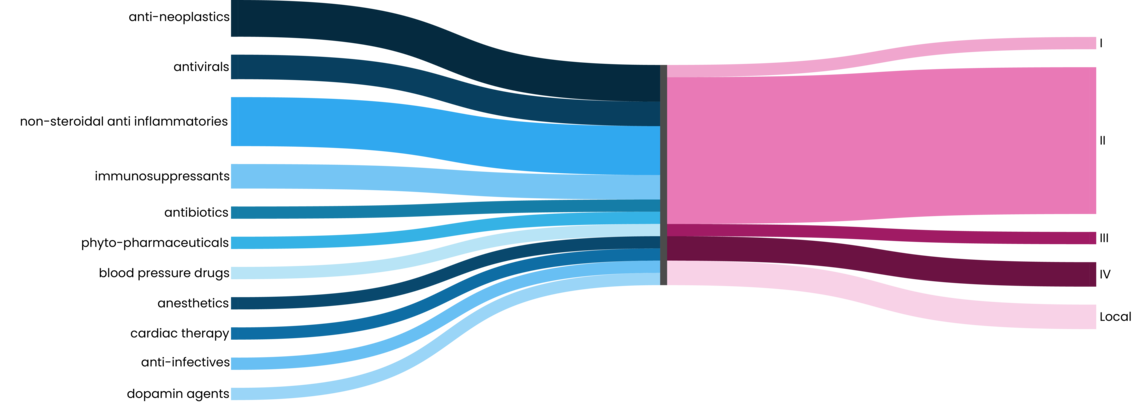
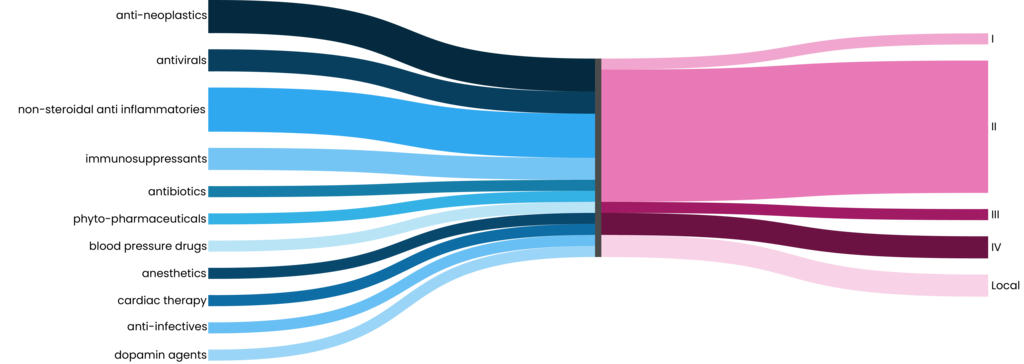
BCS Classes:
I (high solubility, high permeability)
II (low solubility, high permeability)
III (high solubility, low permeability)
IV (low solubility, low permeability)
Local (topical used only)
